Computer vision: the ultimate guide on the 4 main tasks
Thanks to computer vision, computers can recognize what they observe by performing many tasks. Let’s know the most important ones!
Computer vision: the ultimate guide on the 4 main tasks
Thanks to computer vision, computers can recognize what they observe by performing many tasks. Let’s know the most important ones!
Vision allows to interpret everything we see. We assign a name to an object and thus we define it. Computer vision can perform this task and many others.
Four are the most popular tasks it performs, but despite this, there is still some confusion.
With this guide, the goal is to make their differences more clear.
Computer vision: what is it and how does it work?
One of man’s five main senses is undoubtedly sight. Are living beings the only ones who have it?
Vision allows us to perceive and to interpret things. We see things as they are because of our eyes, by how they detect light and then coordinate with the brain to turn light into images.
This is our vision, human vision, but we are not the only ones who possess it. There is, in fact, another kind of vision, which is computer vision.
Let’s find out more.
Computer vision is a field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that enables computers to observe and to understand the content of photos and videos. But how is it possible? How does the process work?
Essentially algorithms are used to gather characteristics of human vision and to generate models to emulate our capabilities in computers.
Computer vision performs data analysis multiple times until it can recognize images. To achieve the final result. Deep learning, a type of machine learning, uses in particular convolutional neural networks (CNN).
CNNs need a large amount of labeled data in order to distinguish correctly their target.
They use convolutions, a mathematical operation, to learn a large amount of patterns in the train images. Then, CNNs use these features just extrapolated to achieve its predictions.
Thanks to great advances in Artificial Intelligence, computer vision is getting better and better in accuracy. How so?
One of the main factors behind its growth is related to the amount of data we generate that is used to train algorithms. The more data used, the better the performance.
The four main tasks of computer vision
Speaking of performance, there are so many tasks that we humans perform almost unconsciously that we rarely notice. However, for a computer to learn how to perform these things is difficult. It is difficult, but not impossible.
The main tasks of computer vision are Image Classification, Object Detection, Semantic Segmentation and Instance Segmentation. Even today, many people do not have a clear idea of these concepts.
Let’s go step by step by looking at these images and what they convey.
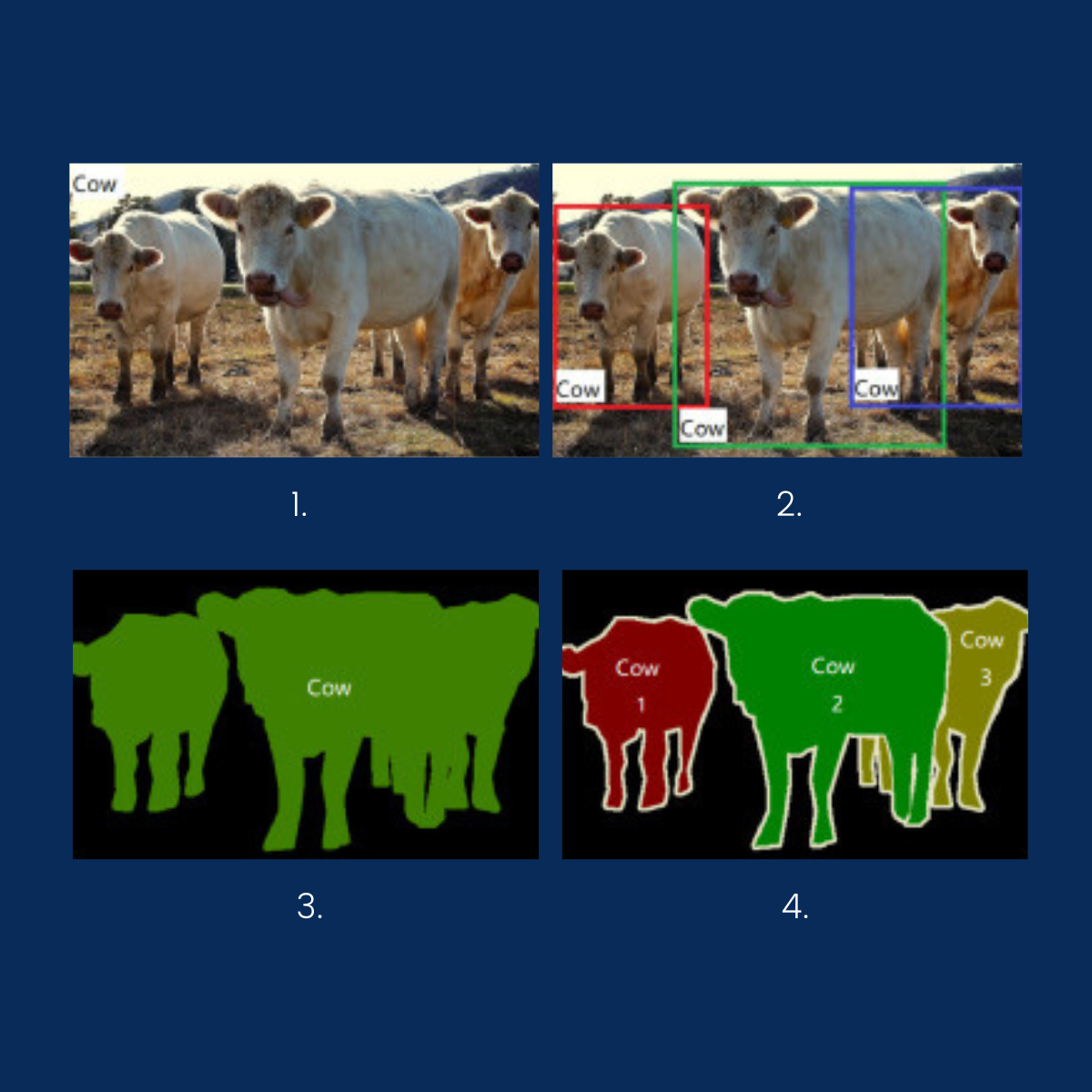

- In the first image, there are cows.
- Next, cows are recognized and located in the picture.
- Here, cows are detected and located in the space without distinguishing instances.
- In the last case, all objects in the picture are identified as cows, belonging to the same class with different instances.
Once we have described the images, it is time to assign specific names to each of them. Here they are below.

|
Computer vision tasks
|
Now it will certainly be easier to associate the task with the image. Let’s go into more detail and find out how they actually work.
- Image classification means identifying the class to which the object belongs. For example, there are objects that belong to various classes such as dogs, cats, etc. The deep learning model will determine that the animal detected in the image belongs to the cow class with the highest probability.
- Object detection enables the detection of objects in an image and their spatial location. Bounding boxes, that are rectangles, are used to delimit the object within them.
- As for Semantic Segmentation, it is able to identify similar objects in the image that belong to the same class at the pixel level. The similar objects are colored in the same way to symbolize belonging to the same class.
- Finally, Instance Segmentation recognizes the different instances given in the image with their boundaries at the deep pixel level.
As we can see, each task increases its capabilities and is able to detect additional details of objects in the image.
Recent updates in the field: new tasks
We just described four of the main tasks tackled by computer vision but the list doesn’t finish here. During recent years at least two more fields expanded abruptly:
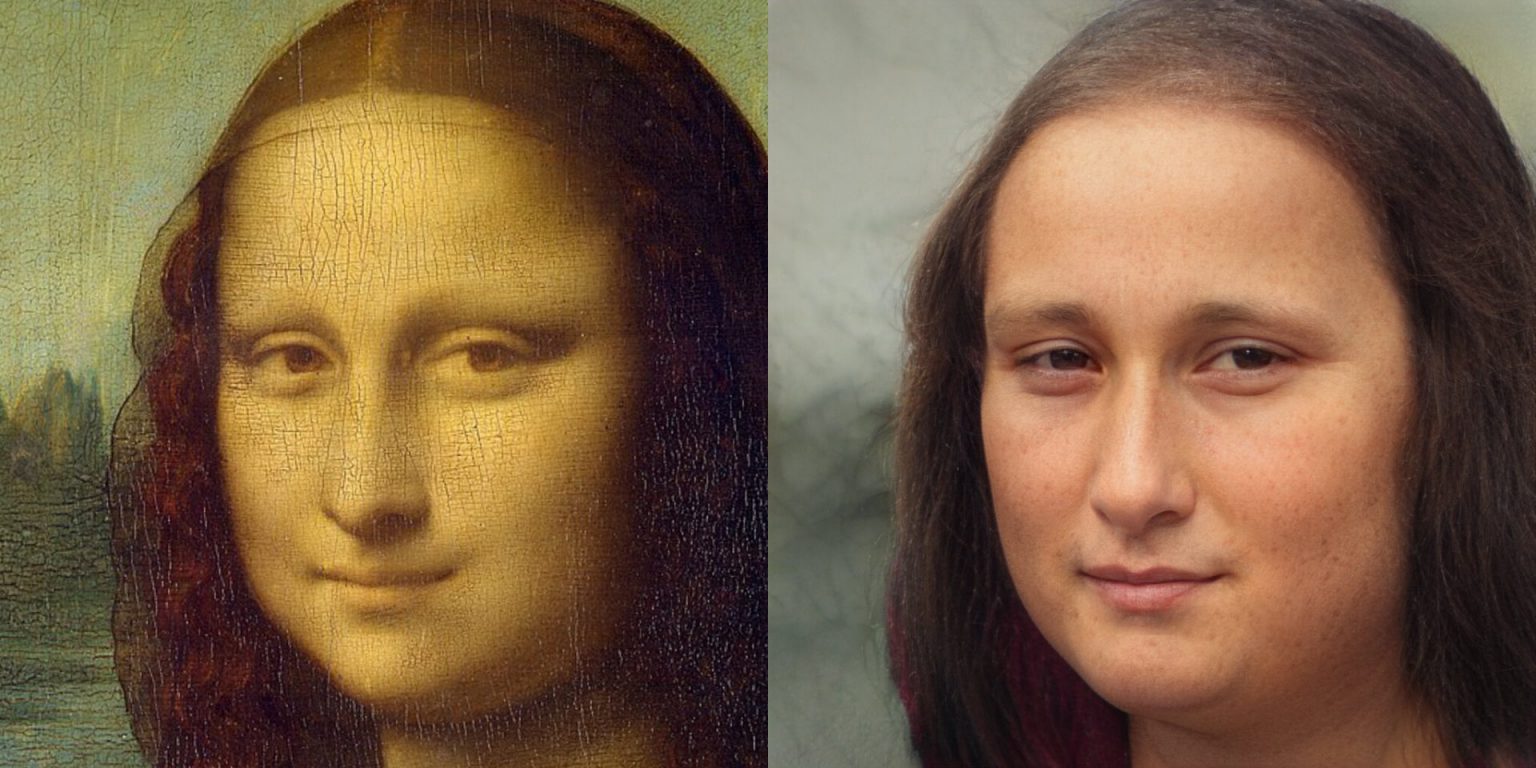
- Data Generation: By learning the distribution of a dataset using approaches like GANs (generative adversarial networks), it is possible to generate new images that look real and can be used in new datasets. This task allows to takle the most important limitation of deep learning: the amount of data needed to train a model. An explanatory and shocking example involves these images that at first glance might be pictures of simple people. This is not the case at all, as they are images of AI-generated people who don’t exist in reality.
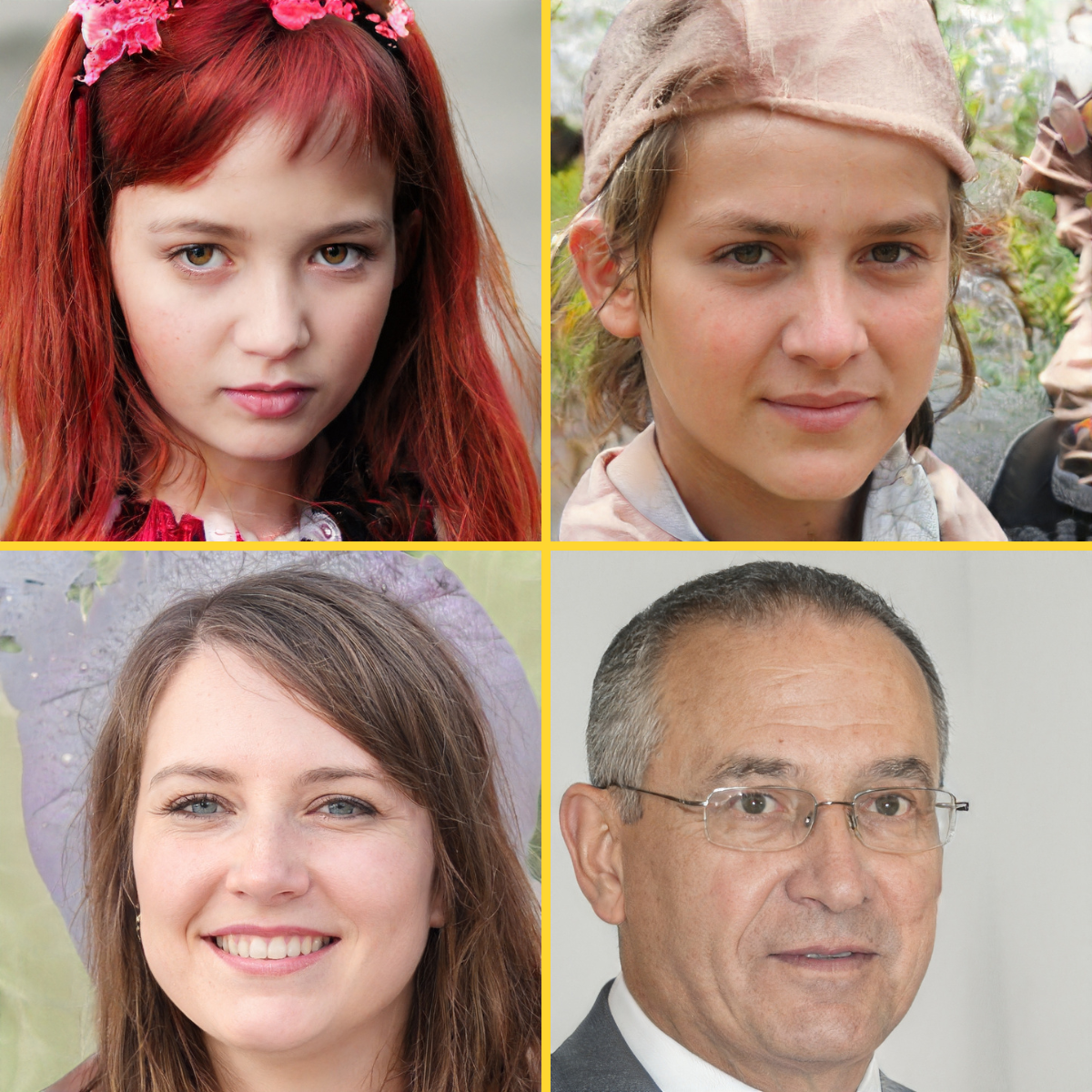

|
AI-generated images of people |
- Domain adaptation: Approaches like GANs can be used to transform images from a source domain to a target domain. This is very beneficial for generalizing networks’ performance on different tasks without annotating new data. Applications like Deepfakes belong here, that is a technology that allows to replace the likeness of one person with another in a video. In many movies and in real life, deepfake is used.
As we explored in this article, computer vision is moving forward.
Scientists started to tackle supervised learning (the 4 main tasks we focused on) in the late 80s. Now the real challenge is to apply unsupervised learning, aiming to help the computer to generalize all by itself what it is seeing. Day by day new challenges appear and new solutions are developed all around the world.
Who knows in the future what Artificial Intelligence will be more skilled at than we are. Stay tuned for new updates.
© Copyright 2012 – 2023 | All Rights Reserved
Author: Niccolò Cacciotti, Head of AI Department
Vision allows to interpret everything we see. We assign a name to an object and thus we define it. Computer vision can perform this task and many others.
Four are the most popular tasks it performs, but despite this, there is still some confusion.
With this guide, the goal is to make their differences more clear.
Computer vision: what is it and how does it work?
One of man’s five main senses is undoubtedly sight. Are living beings the only ones who have it?
Vision allows us to perceive and to interpret things. We see things as they are because of our eyes, by how they detect light and then coordinate with the brain to turn light into images.
This is our vision, human vision, but we are not the only ones who possess it. There is, in fact, another kind of vision, which is computer vision.
Let’s find out more.
Computer vision is a field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that enables computers to observe and to understand the content of photos and videos. But how is it possible? How does the process work?
Essentially algorithms are used to gather characteristics of human vision and to generate models to emulate our capabilities in computers.
Computer vision performs data analysis multiple times until it can recognize images. To achieve the final result. Deep learning, a type of machine learning, uses in particular convolutional neural networks (CNN).
CNNs need a large amount of labeled data in order to distinguish correctly their target.
They use convolutions, a mathematical operation, to learn a large amount of patterns in the train images. Then, CNNs use these features just extrapolated to achieve its predictions.
Thanks to great advances in Artificial Intelligence, computer vision is getting better and better in accuracy. How so?
One of the main factors behind its growth is related to the amount of data we generate that is used to train algorithms. The more data used, the better the performance.
The four main tasks of computer vision
Speaking of performance, there are so many tasks that we humans perform almost unconsciously that we rarely notice. However, for a computer to learn how to perform these things is difficult. It is difficult, but not impossible.
The main tasks of computer vision are Image Classification, Object Detection, Semantic Segmentation and Instance Segmentation. Even today, many people do not have a clear idea of these concepts.
Let’s go step by step by looking at these images and what they convey.

- In the first image, there are cows.
- Next, cows are recognized and located in the picture.
- Here, cows are detected and located in the space without distinguishing instances.
- In the last case, all objects in the picture are identified as cows, belonging to the same class with different instances.
Once we have described the images, it is time to assign specific names to each of them. Here they are below.

|
Computer vision tasks
|
Now it will certainly be easier to associate the task with the image. Let’s go into more detail and find out how they actually work.
- Image classification means identifying the class to which the object belongs. For example, there are objects that belong to various classes such as dogs, cats, etc. The deep learning model will determine that the animal detected in the image belongs to the cow class with the highest probability.
- Object detection enables the detection of objects in an image and their spatial location. Bounding boxes, that are rectangles, are used to delimit the object within them.
- As for Semantic Segmentation, it is able to identify similar objects in the image that belong to the same class at the pixel level. The similar objects are colored in the same way to symbolize belonging to the same class.
- Finally, Instance Segmentation recognizes the different instances given in the image with their boundaries at the deep pixel level.
As we can see, each task increases its capabilities and is able to detect additional details of objects in the image.
Recent updates in the field: new tasks
We just described four of the main tasks tackled by computer vision but the list doesn’t finish here. During recent years at least two more fields expanded abruptly:
- Data Generation: By learning the distribution of a dataset using approaches like GANs (generative adversarial networks), it is possible to generate new images that look real and can be used in new datasets. This task allows to takle the most important limitation of deep learning: the amount of data needed to train a model. An explanatory and shocking example involves these images that at first glance might be pictures of simple people. This is not the case at all, as they are images of AI-generated people who don’t exist in reality.

|
AI-generated images of people |
- Domain adaptation: Approaches like GANs can be used to transform images from a source domain to a target domain. This is very beneficial for generalizing networks’ performance on different tasks without annotating new data. Applications like Deepfakes belong here, that is a technology that allows to replace the likeness of one person with another in a video. In many movies and in real life, deepfake is used.
As we explored in this article, computer vision is moving forward.
Scientists started to tackle supervised learning (the 4 main tasks we focused on) in the late 80s. Now the real challenge is to apply unsupervised learning, aiming to help the computer to generalize all by itself what it is seeing. Day by day new challenges appear and new solutions are developed all around the world.
Who knows in the future what Artificial Intelligence will be more skilled at than we are. Stay tuned for new updates.
© Copyright 2012 – 2023 | All Rights Reserved
Author: Niccolò Cacciotti, Head of AI Department











Leave A Comment